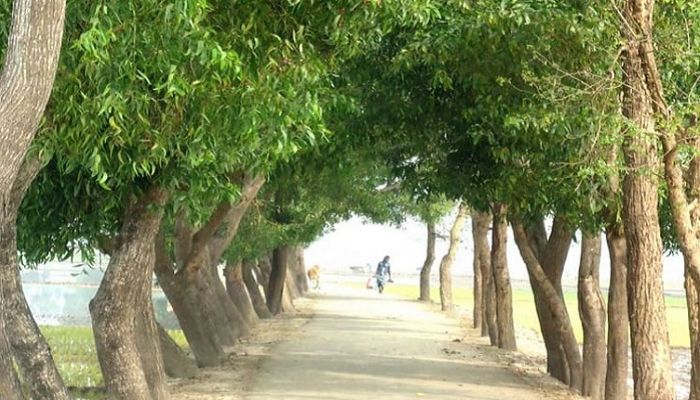
1,800-kilometre strip plantation raised in northern region
BSS : Strip plantations on 1,800-kilometre of land have been raised with varieties of eco-friendly fruit, forest and herbal trees creating eco-tourism facilities.
Besides 130 ponds, canals and beels were either excavated or re-excavated to attain the goals of expediting the eco-restoration process.
The promotional activities were implemented on behalf of a project titled “Eco-Restoration of the Northern Region of Bangladesh” in all 16 districts under Rajshahi and Rangpur divisions recently.
The Department of Social Forestry (DSF) has implemented the project with the main thrust of checking desertification in the country’s northwest region besides conserving biodiversity and other surrounding environment through a massive tree-sapling transplantation.
The scheme also promoted uses of surface water after reducing the gradually mounting pressure on groundwater through excavating and re-excavating derelict ponds and other water bodies.
Divisional Forest Officer Muhammad Rafiquzzaman told BSS that the four-year project has been implemented with an estimated cost of around Tk 247.9 million for establishing plantations aimed at biodiversity enhancement.
He said they have transplanted tree-saplings on more than 200-kilometer area under the project and the poor and underprivileged people were engaged in the project activities for improving their socio-economic condition.
The programme increased the number of surface water reservoirs using derelict water bodies to promote sustainable utilisation for facilitating irrigation, maintaining a near constant water table, domestic use and watering of forest nurseries.
It has also increased tree coverage for biodiversity conservation and wildlife habitat restoration, and supply of raw materials contributing to the local firewood needs.
As a whole, the profitable afforestation activities are contributing a lot towards encouraging many people in planting adequate saplings of wood, medicinal and fruit- bearing plants at homesteads, roadsides, office premises, embankments, forest areas, religious institutions’ premises and other places.
It has also created a sustainable employment generation for the poor women, landless population, destitute and underprivileged young generation.
Muhammad Rafiquzzaman said emphasis is being given to increasing the number of fruit and other tree cover area, timber production awareness and community participation in conservation and production.
The issue of raising awareness and capacity building among the community relating to land degradation and desertification will be given priority during implementation of the programme.
Significant numbers of small and marginal farmers are seen attaining economic emancipation through participatory intervention. The project is helping restoration of plant and habitat biodiversity alongside increasing economic activities and employment opportunities.
Besides, the social forestry programme supplementing the government’s poverty reduction effort together with facing the adverse impact of climate change in the drought-prone area.
Currently, social forestry is being judged as a tool for bringing about ecological and socioeconomic improvements. It also contributes to alleviating poverty in the dried region.
Many of the newly created gardens on various vacant places like river embankment, railway land, char area and roadside land are now eye-catching.
Positive ecological changes refer to a greater number of trees, more biomass production and beneficial ecological effects. Mass awareness is being built up regarding planting more trees on all the vacant spaces.
Rafiquzzaman said they are working on using surface water for irrigation purposes to ensure lessening the exorbitant pressure on ground water.